IT
Menu | GSP | LiveMath
TRANSFORMATION IT LESSON 2 - ROTATION
(SEC 4 ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS)
Software: JavaSketchpad (JSP) – need
Geometer's Sketchpad (GSP)
Thinking Skills: Induction and
Deduction
At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
(1) infer by induction the property of the image under a rotation,
(2) construct the image under a rotation about any centre,
(3) derive formulae for the coordinates of the image under rotations
of 90o, 180o and 270o anticlockwise about
the origin,
(4) find the invariant point under a rotation,
(5) find the centre of rotation given an object and its image.
A. PROPERTY OF IMAGE UNDER ROTATION
It takes a few seconds to initialise the JavaSketch below. But if the
toolbar at the bottom reads, "Applet not found", click
here to troubleshoot.
|
| 1. |
The first JavaSketch (IT4EMTransfRotation1.gsp) shows a
triangle ABC and its image A'B'C' under a rotation of 90o anticlockwise
about the centre O. Observe the shapes and sizes of the object and the
image. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Move the points A, B and C anywhere. Try making the object ABC an equilateral
triangle, an isosceles triangle, a scalene triangle and a right-angled
triangle. Observe the shapes and sizes of the object and the image. |
| |
|
| 3. |
You can also move the centre of rotation anywhere. Once
again, observe the shapes and sizes of the object and the image. |
|
| |
|
| Question 1: |
Infer by induction
the shape and size of the image under a rotation.
|
| |
Such a transformation that preserves the shape and size of the object
is called an __________ transformation. |
| |
|
| Question 2: |
What do you observe about angle AOA', the angle between
the line joining the object A to the centre O and the line joining the
centre O to the image A'?
Angle AOA' = ____o = Angle of ____________. |
| |
This property will help you to construct the
image of an object under a rotation. |
B. ROTATION OF 90 DEGREES ANTICLOCKWISE
JavaSketchpad cannot support grid
lines, so you have to open the GSP file (IT4EMTransfRotation2.gsp)
using the Geometer's
Sketchpad software which has a free evaluation version. Click on
the hyperlink above and choose the option "Open it" instead of "Save it
to disk". If you are using GSP for the first time,
a dialogue box "Open With" will appear. If you don't know what to do, click
here. The diagram below is just a non-interactive picture of the
sketch.
 |
| 1. |
The second sketch (IT4EMTransfRotation2.gsp) shows a triangle
ABC with the origin O as the centre of rotation. The coordinates of the
vertices are A(–3,4), B(–4,2) and C(–1,1). The angle of rotation is set
as 90o anticlockwise. Using the property
in Question 2, write down the vertices of the image in the table
in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
| |
|
| 3. |
Double-click the button "Hide Image".
Then move the vertices of the triangle to A(1,3), B(–3,1) and C(–1,–2).
Write down the vertices of the image in the table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 4. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
|
| |
|
| Question 3: |
By observing the coordinates of the 6 points and their
images, derive a formula for the coordinates of an image under a rotation
of 90o anticlockwise about the origin O.
The point P(x, y) is mapped onto the image P'(___ , ___). |
C. ROTATION OF 90 DEGREES CLOCKWISE
JavaSketchpad cannot support grid
linesm, so you have to open the GSP file (IT4EMTransfRotation3.gsp)
using the Geometer's
Sketchpad software which has a free evaluation version. Click on
the hyperlink above and choose the option "Open it" instead of "Save it
to disk".
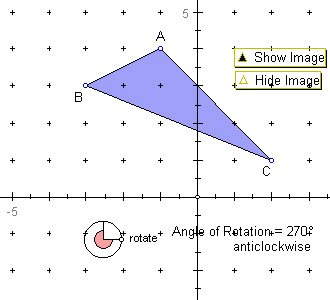 |
| 1. |
The third sketch (IT4EMTransfRotation3.gsp) shows a triangle
ABC with the origin O as the centre of rotation. The coordinates of the
vertices are A(–1,4), B(–3,3) and C(2,1). The angle of rotation is set
as 270o anticlockwise or 90o clockwise. Write down
the vertices of the image in the table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
| |
|
| 3. |
Double-click the button "Hide Image".
Then move the vertices of the triangle to A(1,3), B(–3,–2) and C(0,0).
Write down the vertices of the image in the table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 4. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
|
| |
|
| Question 4: |
By observing the coordinates of the 6 points and their
images, derive a formula for the coordinates of an image under a rotation
of 90o clockwise about the origin O.
The point P(x, y) is mapped onto the image P'(___ , ___). |
| |
|
| Question 5: |
What do you notice about the image of the point C(0,0) in the second
triangle in Paragraph 3 above?
|
|
Such a point is called an _____________ point. It will always lie on
the ________ of _____________ . |
D. ROTATION OF 180 DEGREES (HALF-TURN)
JavaSketchpad cannot support grid
lines, so you have to open the GSP file (IT4EMTransfRotation4.gsp)
using the Geometer's
Sketchpad software which has a free evaluation version. Click on
the hyperlink above and choose the option "Open it" instead of "Save it
to disk".
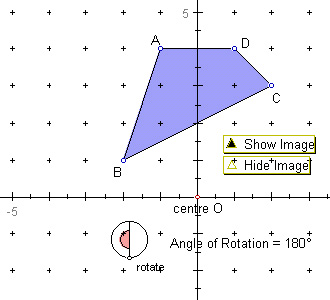 |
| 1. |
The fourth sketch (IT4EMTransfRotation4.gsp) shows a quadrilateral
ABCD with the origin O as the centre of rotation. The coordinates of the
vertices are A(–1,4), B(–2,1), C(2,3) and D(1,4). The angle of rotation
is set as 180o. Write down the vertices of the image in the
table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
| |
|
| 3. |
Double-click the button "Hide Image".
Then move the vertices of the quadrilateral to A(–1,3), B(–2,2), C(0,0)
and D(2,2). Write down the vertices of the image in the table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 4. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
|
| |
|
| Question 6: |
By observing the coordinates of the 8 points and their
images, derive a formula for the coordinates of an image under a rotation
of 180o about the origin O.
The point P(x, y) is mapped onto the image P'(___ , ___). |
| |
|
| Question 7: |
Which vertex of the second quadrilateral is invariant?
|
E. ROTATION ABOUT CENTRE OTHER THAN
THE ORIGIN
JavaSketchpad cannot support grid
lines, so you have to open the GSP file (IT4EMTransfRotation5.gsp)
using the Geometer's
Sketchpad software which has a free evaluation version. Click on
the hyperlink above and choose the option "Open it" instead of "Save it
to disk".
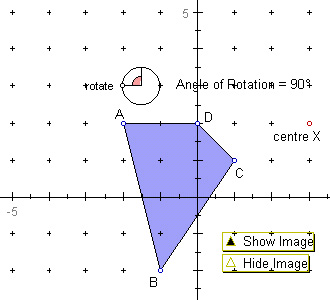 |
| 1. |
The fifth sketch (IT4EMTransfRotation5.gsp) shows a quadrilateral
ABCD with the point X(3,2) as the centre of rotation. The coordinates of
the vertices are A(–2,2), B(–1,–2), C(1,1) and D(0,2). The angle of rotation
is set as 90o anticlockwise. Write down the vertices of the
image in the table in the Worksheet. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Double-click the button "Show Image" to check your answers. |
| |
|
| 3. |
Change the angle of rotation by moving the point "rotate" at the top
left hand corner. Observe how the image moves for different angles of rotation. |
|
| |
|
| Question 8: |
By observing the coordinates of the 4 points and their
images, do you notice any pattern that will enable you to derive a formula
for the coordinates of an image under a rotation of 90o about
the point X(3,2)?
|
F. HOW TO FIND CENTRE OF ROTATION
JavaSketchpad cannot support grid
lines, so you have to open the GSP file (IT4EMTransfRotation6.gsp)
using the Geometer's
Sketchpad software which has a free evaluation version. Click on
the hyperlink above and choose the option "Open it" instead of "Save it
to disk".
If you are using GSP Version 4,
open this file:
IT4EMTransfRotation6_v4.gsp.
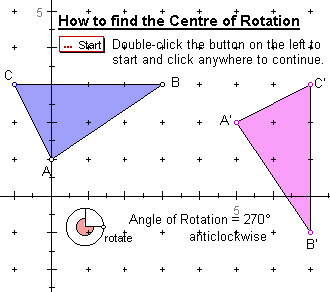 |
| 1. |
The sixth sketch (IT4EMTransfRotation6.gsp) shows a triangle
ABC and its image A'B'C' under a rotation of 90o clockwise.
The coordinates of the vertices of the object and the image are A(0,1),
B(3,3), C(–1,3), A'(5,2), B'(7,–1) and C'(7,3) respectively. |
| |
|
| 2. |
Double-click the button "Start" to show how to find the centre of rotation.
It will stop at each step. Click anywhere to continue. |
|
| |
|
| Question 9: |
State the coordinates of the centre of rotation.
|
| |
|
| Question 10: |
Move the vertices of triangle ABC anywhere. The image will move accordingly.
Change the angle of rotation to 90o anticlockwise. Double-click
the button "Start" to find the centre of rotation. State its coordinates.
|
| |
|
| Question 11: |
Summarise the 5 steps needed to find the centre of rotation.
Step 1: __________________________________________
Step 2: __________________________________________
Step 3: __________________________________________
Step 4: __________________________________________
Step 5: __________________________________________ |
| |
|
| Question 12: |
Change the angle of rotation to 180o. Double-click the button
"Start" to find the centre of rotation. What do you notice about the point
of intersection of the lines AA' and BB'?
|
| |
|
| Question 13: |
If the angle of rotation to 180o, how do you simplify the
method in Question 11 to find the centre of rotation?
Step 1: __________________________________________
Step 2: __________________________________________
Step 3: __________________________________________ |
| |
|
| Question 14: |
If there is an invariant point under a rotation, how do you find the
centre of rotation?
|
| |
|
| Note: |
There are 3 ways to find the centre of rotation, depending
on the angle of rotation and the image:
| (i) |
If there is an invariant point, see Question 14. |
| (ii) |
If angle of rotation = 180o, see Question 13. |
| (iii) |
For the general method, see Question 11. |
|
IT Menu |
GSP
| LiveMath




